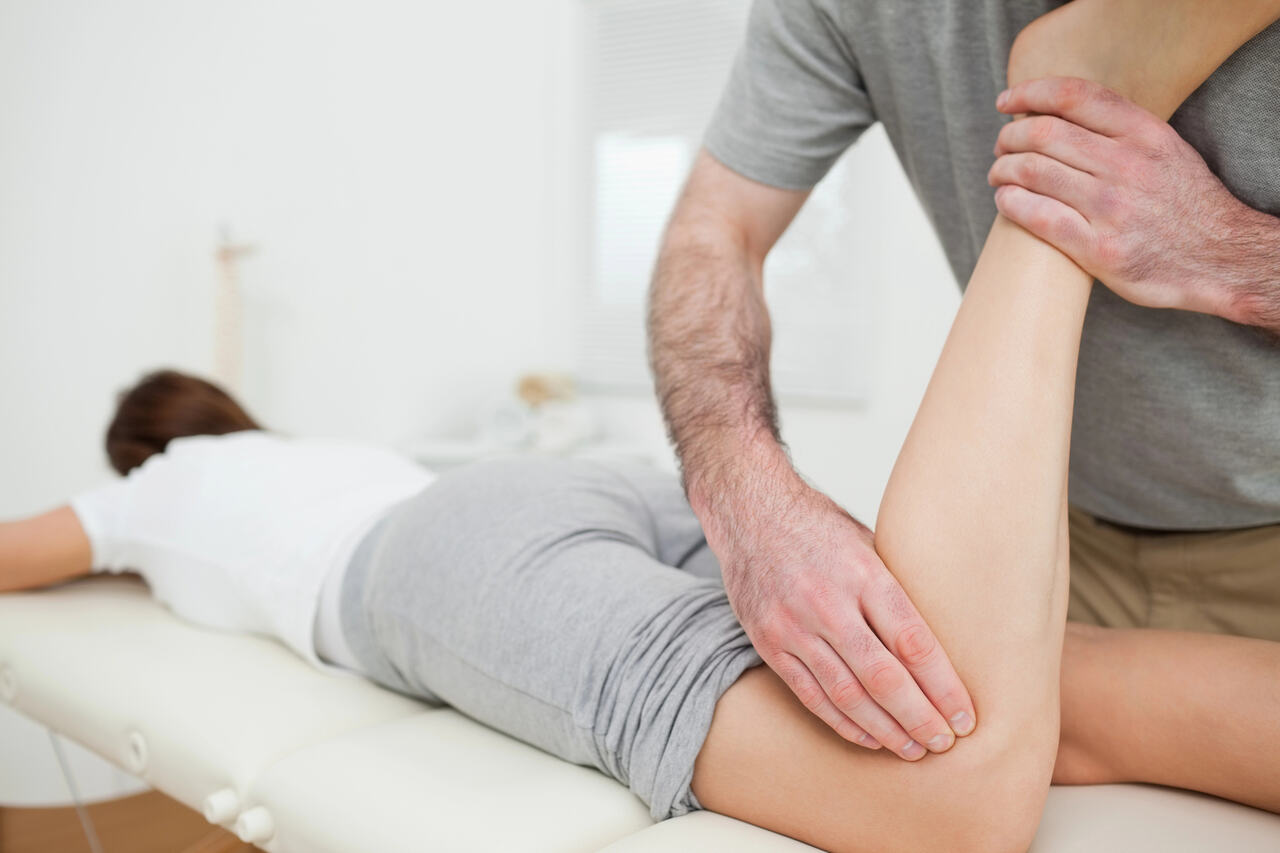
Unraveling Osteopathy
Introduction to Osteopathy
Osteopathy is a unique form of healthcare that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of a wide range of health conditions. It is grounded in the principle that the well-being of an individual heavily relies on the proper functioning of their bones, muscles, ligaments, and connective tissues. Osteopaths use manual techniques to encourage optimal health by enhancing the body’s own healing processes.
Osteopathy places a strong emphasis on patient-centered care. Practitioners take into account not just physical symptoms but also psychological and social factors that can affect health. This holistic approach aims to treat the whole person, rather than just the symptoms, making it a popular choice for many seeking well-rounded healthcare solutions.
Understanding what osteopathy entails can help individuals make informed decisions about their health. Osteopathy has gained recognition for its effectiveness in managing conditions such as back pain, neck pain, and even posture-related issues.
Historical Context of Osteopathy
Osteopathy was founded in the late 19th century by Andrew Taylor Still, an American physician who saw the need for a more holistic approach to medicine. Disillusioned by the limitations of conventional treatments of the time, Still developed a system that emphasized the musculoskeletal framework’s key role in overall health and well-being.
In 1892, Still established the first school of osteopathy in Kirksville, Missouri, laying the foundation for what would become a globally recognized healthcare practice. Over the years, osteopathy has evolved, incorporating advances in medical science while maintaining its core principles.
Today, osteopathy blends traditional techniques with modern medical knowledge to offer a comprehensive approach to healthcare. This practice has expanded to address a wide variety of conditions, from musculoskeletal issues to chronic pain management and even TMJ disorders.
Understanding this historical backdrop can provide valuable context for appreciating the principles and techniques used in osteopathy treatment today.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1874 | Andrew Taylor Still develops osteopathic principles |
| 1892 | First osteopathy school opens in Kirksville, Missouri |
| Early 1900s | Osteopathy gains recognition and expands globally |
| Present Day | Osteopathy integrates modern medicine with traditional principles |
By delving into the roots and evolution of osteopathy, individuals can better understand its unique approach to healthcare, distinguishing it from other practices such as chiropractic care and physical therapy.
Core Principles of Osteopathy
Osteopathy is based on several core principles that guide its approach to treating patients. Understanding these principles will help clarify what osteopathy is and how it works.
Holistic Approach to Health
Osteopathy adopts a holistic approach to health, focusing on the whole body rather than isolated symptoms. This means considering the body’s structure and functions as interconnected components. Osteopaths believe that the body has an intrinsic ability to heal itself, and their role is to facilitate this natural process.
Osteopathic practitioners assess various aspects of a patient’s life, including physical, emotional, and environmental factors. This comprehensive perspective ensures that all factors contributing to a condition are addressed, promoting overall health and well-being.
Principles of Osteopathic Treatment
Osteopathy operates on several key principles:
- The Body is a Unit: The human body functions as a single entity, and disturbances in one part can affect the whole.
- Structure and Function are Interrelated: Proper alignment and function of the musculoskeletal system are crucial for overall health.
- Self-Healing Mechanisms: The body has the inherent ability to heal itself, and osteopathic treatment aims to support these natural processes.
These principles guide osteopaths in diagnosing and treating their patients, ensuring a personalized and effective approach.
Osteopathic Techniques
Various techniques are employed in osteopathy to address bodily imbalances and support healing. These can be broadly categorized into manipulative and non-manipulative techniques.
Manipulative Techniques
These techniques involve hands-on manipulation of muscles, bones, and joints to improve mobility, reduce pain, and promote healing.
- Soft Tissue Manipulation: Focuses on muscles, tendons, and ligaments to relieve tension and improve circulation.
- Joint Articulation: Tackles restricted joint movement by gently moving the joints through their range of motion.
- High-Velocity Low-Amplitude (HVLA) Thrusts: Quick, precise movements that aim to restore normal joint function.
| Technique | Purpose | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Soft Tissue Manipulation | Relax muscles, Enhance circulation | Osteopathy for back pain |
| Joint Articulation | Improve joint mobility | Osteopathy for neck pain |
| HVLA Thrusts | Restore joint function | Osteopathy for herniated disc |
Non-manipulative Techniques
- Cranial Osteopathy: Involves gentle pressure on the skull and spine to release tension and improve function.
- Visceral Osteopathy: Targets internal organs to enhance their function and reduce pain.
Explore more about these techniques in our detailed article on osteopathy techniques.
By following these core principles and techniques, osteopathy aims to provide holistic and effective care for a wide range of conditions. To learn more about what osteopathy can treat, visit our sections on osteopathy for tmj, osteopathy for sciatica, and osteopathy for headaches.
What Conditions Osteopathy Can Address
Osteopathy is a versatile healthcare practice that can address a range of conditions. These include musculoskeletal issues, pain management, and other health conditions.
Musculoskeletal Issues
Osteopathy is particularly effective for treating musculoskeletal problems. This includes issues related to bones, muscles, ligaments, and joints.
- Back Pain: Osteopaths often treat back pain using techniques to alleviate discomfort and restore function. For more detailed information, read our article on osteopathy for back pain.
- Neck Pain: Techniques used can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Learn more about osteopathy for neck pain.
- Hip Pain: Addressing hip pain through manipulation and other methods is common. Visit osteopathy for hip pain for details.
- Shoulder Pain: Effective techniques for pain relief and increased range of motion. Check osteopathy for shoulder pain.
- Knee Pain: Treating knee issues through targeted techniques. See osteopathy for knee pain.
Pain Management
Osteopathy is also effective in managing various types of pain beyond musculoskeletal issues.
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Headaches/Migraines | Techniques to alleviate tension and improve blood flow. See osteopathy for headaches. |
| Sciatica | Treatment to relieve nerve pain in the legs. Read osteopathy for sciatica. |
| Fibromyalgia | Techniques to relieve muscle pain and fatigue. Explore osteopathy for fibromyalgia. |
| TMJ Disorders | Techniques to relieve jaw pain and improve function. Learn more about osteopathy for tmj. |
Other Health Conditions
Osteopathy can also be beneficial for various other health conditions, addressing issues that affect overall well-being.
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Herniated Disc | Techniques to alleviate pressure and improve mobility. Details at osteopathy for herniated disc. |
| Arthritis | Strategies to reduce pain and increase joint mobility. See osteopathy for arthritis. |
| Scoliosis | Methods to improve spinal alignment and reduce discomfort. Read osteopathy for scoliosis. |
| Plantar Fasciitis | Techniques to relieve foot pain and improve movement. Explore osteopathy for plantar fasciitis. |
| Posture Issues | Addressing poor posture to alleviate associated pain. Visit osteopathy for posture. |
By understanding the range of conditions osteopathy can address, you can better appreciate its versatility and effectiveness. For an overview of osteopathic techniques, check out our article on osteopath treatment.
Osteopathy vs. Other Healthcare Practices
To better understand what osteopathy is, it’s useful to compare it to other healthcare practices. This section explores how osteopathy differs from chiropractic care, physical therapy, and traditional medicine.
Contrasts with Chiropractic Care
Osteopathy and chiropractic care both focus on manual manipulation of the body, but they have distinctive approaches and philosophies.
| Aspect | Osteopathy | Chiropractic Care |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Holistic body treatment involving muscles, joints, and spine | Primarily spinal adjustments |
| Techniques | Soft tissue techniques, stretching, mobilizations | Adjustments and spinal manipulations |
| Philosophy | Emphasizes the body’s self-healing ability, overall well-being | Focuses on correction of spinal alignment to address ailments |
| Training | Broad medical training including pharmacology, surgery | Specialized training in chiropractic adjustments |
Osteopathy’s holistic approach considers the entire body, whereas chiropractic care primarily targets the spine. For more detailed differences, visit our article on osteopathy versus chiropractic.
Distinctions from Physical Therapy
While both osteopathy and physical therapy aim to improve mobility and reduce pain, their methodologies and focuses have distinguishing elements.
| Aspect | Osteopathy | Physical Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Holistic, including body’s structural and functional aspects | Focuses on rehabilitation and functional improvement of specific areas |
| Techniques | Manual techniques, lifestyle counseling | Exercises, manual therapy, electrotherapy |
| Scope | Addresses body as a whole, integrated system | Targets specific regions, conditions or injuries |
| Philosophy | Body’s self-regulating mechanisms | Functional recovery and optimization of movement patterns |
Osteopaths use a mix of hands-on techniques and lifestyle advice, whereas physical therapists primarily use rehabilitative exercises. Visit our page on osteopath treatment to see how an osteopath works.
Comparisons with Traditional Medicine
Osteopathy and traditional medicine often overlap in their goal to improve health, but their concepts and treatment modalities are quite different.
| Aspect | Osteopathy | Traditional Medicine |
|---|---|---|
| Principles | Body’s self-healing mechanisms, structural and functional integration | Disease-oriented, often involving pharmaceutical and surgical interventions |
| Techniques | Manual osteopathic techniques, advice on lifestyle | Prescriptions, surgeries, and disease-specific treatments |
| Approach | Prevention and holistic care | Diagnosis and treatment of specific conditions |
| Training | Includes general medical education, extensive training in osteopathic techniques | Medical school training, specializes in various fields |
Osteopathy’s emphasis is on prevention and whole-body health, while traditional medicine is more disease-specific and interventionist. If you’re curious about the benefits of osteopathy, you can find more information in our dedicated article.
Internal Links for Further Reading
- osteopathy
- osteopathy versus chiropractic
- osteopath treatment
- benefits of osteopathy
- osteopathy techniques
Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions about which healthcare approach might be best for your needs.
How Osteopathy Works
Initial Assessment and Diagnosis
When it comes to osteopathy, the first step is the initial assessment and diagnosis. During this phase, the osteopath conducts a comprehensive evaluation to understand the patient’s condition. The process involves several steps:
- Patient History: The osteopath will ask detailed questions about the patient’s medical history, lifestyle, and any symptoms they are experiencing.
- Physical Examination: This includes a thorough examination of the patient’s posture, mobility, and overall physical condition.
- Diagnostic Tests: Sometimes, additional diagnostic tests such as X-rays or MRIs may be recommended to gain a clearer understanding of the issue.
Below is a typical outline of the initial assessment:
| Assessment Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Patient History | Collecting detailed medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle information. |
| Physical Examination | Evaluating posture, mobility, and physical condition. |
| Diagnostic Tests | Using X-rays, MRIs, or other tests if necessary. |
For individuals looking to understand specific conditions like osteopathy for back pain or osteopathy for knee pain, these initial assessments are crucial.
Treatment Modalities Used in Osteopathy
Osteopathy employs a variety of treatment modalities tailored to each patient’s condition. The techniques used can vary depending on the diagnosis but generally include:
- Soft Tissue Manipulation: Involving massage and stretching to relieve muscle tension and improve circulation.
- Joint Articulation and Mobilization: Techniques to improve range of motion in joints and reduce pain.
- High-Velocity Low-Amplitude Thrusts (HVLA): Quick and precise movements to adjust and realign the spine or other joints.
- Cranial Osteopathy: Gentle techniques focusing on the head and spine.
The table below categorizes some common osteopathic techniques:
| Treatment Modality | Description |
|---|---|
| Soft Tissue Manipulation | Massage and stretching to relieve tension and improve circulation. |
| Joint Articulation | Techniques to enhance joint range of motion. |
| HVLA Thrusts | Quick adjustments for spinal or joint realignment. |
| Cranial Osteopathy | Gentle techniques focusing on the head and spine. |
For more in-depth information on these techniques, visit our article on osteopathy techniques.
Expected Results and Benefits
The benefits of osteopathy are wide-ranging and can address various conditions. Patients often report immediate relief after a session, although multiple sessions might be required for chronic issues. Here are some of the expected results and benefits:
- Pain Relief: Effective for conditions such as osteopathy for neck pain and osteopathy for shoulder pain.
- Improved Mobility: Techniques like joint articulation can enhance range of motion.
- Reduced Muscle Tension: Soft tissue manipulation helps alleviate muscle strain and improve circulation.
- Enhanced Well-being: The holistic approach can lead to overall improved health and well-being.
Here’s a breakdown of the expected benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Pain Relief | Effective for various types of pain, including back, neck, and shoulder pain. |
| Improved Mobility | Enhanced range of motion in joints. |
| Reduced Muscle Tension | Alleviates muscle strain through soft tissue manipulation. |
| Enhanced Well-being | Overall improved health from a holistic approach. |
To explore more about the positive outcomes, check out our guide on the benefits of osteopathy.
Understanding what osteopathy is and how it works can help patients make informed decisions about their healthcare choices. By focusing on tailored assessments and diverse treatment modalities, osteopathy offers a comprehensive approach to improving health and well-being.
Finding an Osteopath
Qualifications and Training
When looking for an osteopath, it’s important to ensure they have the proper qualifications and training. Osteopaths are required to complete extensive education and clinical training, usually involving a bachelor’s degree followed by a Doctor of Osteopathy (DO) degree. This process includes coursework in anatomy, physiology, pathology, and osteopathic techniques, as well as supervised clinical experience.
| Qualification | Description |
|---|---|
| Bachelor’s Degree | Pre-medical or related field |
| Doctor of Osteopathy (DO) | Rigorous program including clinical training |
| Licensing | Required by state |
Upon completion of their education, osteopaths must pass a comprehensive licensing exam to practice. To maintain their license, osteopaths are required to participate in continuing education to stay current with advancements in the field.
Choosing the Right Osteopath
Selecting the right osteopath for your needs involves several considerations. Here are some tips to help you make an informed decision:
- Check Credentials: Verify their education, licensing, and any additional certifications they may hold.
- Experience: Consider their years of practice and specific experience dealing with conditions like back pain, neck pain, or other issues.
- Specializations: Some osteopaths may have specializations in areas such as sciatica, hip pain, or TMJ disorders.
- Consult Reviews: Look for patient reviews or testimonials to gauge their reputation and effectiveness.
What to Expect During an Osteopathic Session
Understanding what happens during an osteopathic session can help alleviate any anxiety. Typically, an initial session includes the following:
Initial Assessment
The osteopath will conduct a thorough assessment, which includes:
- Medical History: A review of your medical history, including any existing conditions like arthritis or scoliosis.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination to assess your posture, mobility, and any areas of pain.
Treatment Plan
Based on the initial assessment, the osteopath will develop a customized treatment plan. This may include various osteopathy techniques tailored to your needs.
Treatment Modalities
Osteopathic treatment often involves hands-on manipulation and other techniques aimed at improving your body’s function. Some common treatments include:
- Soft Tissue Manipulation: To relax and stretch muscles.
- Joint Mobilization: To improve the range of motion.
- Myofascial Release: To alleviate pain and increase mobility.
Patients often wonder what benefits they might experience. Osteopathic treatment can offer a range of benefits, from pain relief to enhanced mobility and overall health improvement.
By understanding the qualifications, selecting the right practitioner, and knowing what to expect during a session, you can make an informed decision about seeking osteopathic care. For more information on how osteopathy can help with specific conditions like headaches or fibromyalgia, explore our related articles.


